Choose the content to read
- What is Lymphoma?
- Types of lymphoma
- What are common lymphoma symptoms?
- What causes lymphoma?
- What are the risk factors of lymphoma?
- How is lymphoma diagnosed?
- How is the treatment for lymphoma?
- Preparing for your appointment
Lymphoma
The lymphatic system, a part of the immune system, includes the lymph nodes, thymus gland, spleen, and bone marrow. It produces white blood cells known as lymphocytes, which fight against foreign microorganisms and prevent diseases and infections. When these lymphocytes mutate, they can become lymphoma.
Types of lymphoma
- Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease)
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is classifiable into many subtypes, depending on the type of cells.
Symptoms
- Swollen lymph nodes, such as in the neck, armpit, stomach, and groin palpable under the skin but are usually painless.
- Swollen lymph nodes in the inner organs, such as the lungs, can cause difficulty breathing or coughs.
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Night sweating
- Lumps
Causes
The possible cause is mutations of lymphocytes leading to malignant transformation.
Risk factors
- Age: Anyone can develop lymphoma.
- Gender: Lymphoma is more common in men than women.
- Impaired immunity: People who take immunosuppressants are at higher risk of developing lymphoma.
- Epstein-Barr virus and Helicobacter pylori infections increase the risk of lymphoma.
Diagnosis
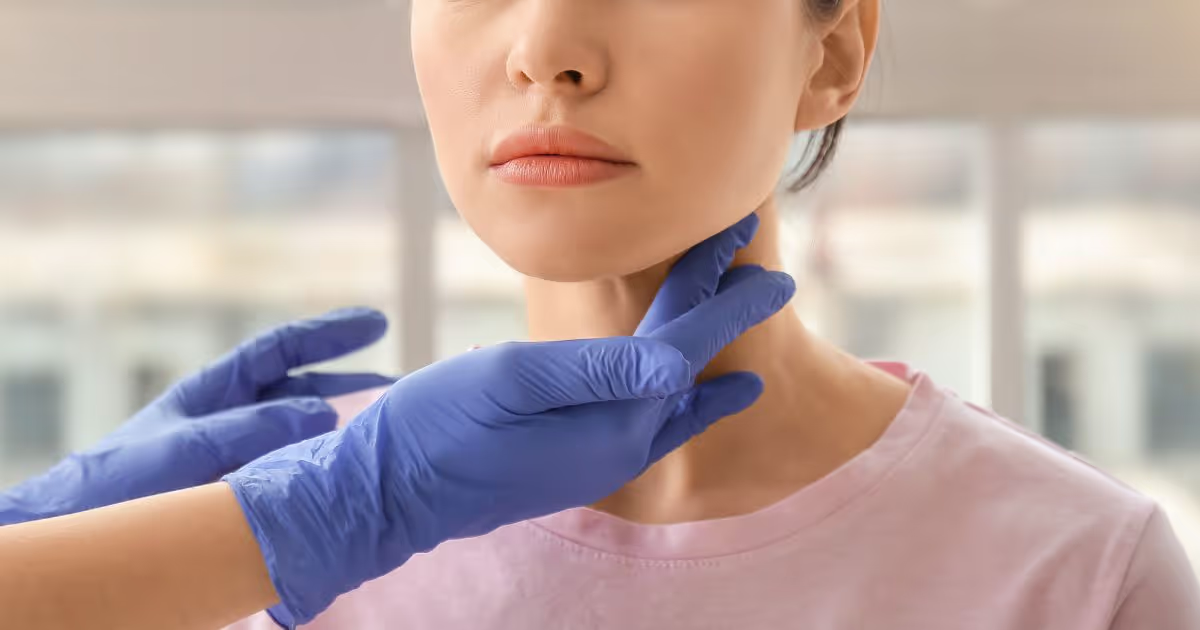
- History taking and physical exam. Your doctor will feel if you have swollen lymph nodes in the neck, underarms, and groin and check for a swollen liver or spleen.
- Blood tests.
- Lymph node biopsy.
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.
- Imaging tests, such as CT, MRI, and PET scans.
A biopsy can identify the type of lymphoma you are developing, improve the accuracy of diagnosis, and help plan effective treatment.
Treatments
An appropriate treatment modality depends on the type and stage of lymphoma and your health. An effective treatment should kill as many cancer cells as possible and keep the disease in remission.
- Monitoring is suitable for slow-growing lymphoma. You may want to wait until you develop symptoms and have periodic doctor appointments to follow up and monitor the condition.
- Radiotherapy aims to destroy cancer cells with the use of a high-energy beam.
- Chemotherapy gives drugs in pill or IV form to kill cancer cells that grow fast.
- Bone marrow transplant or stem cell transplant replaces your bone marrow cells with healthy cells from a donor or yourself.
- Other treatments, such as targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy
Preparation for a doctor's appointment
List all symptoms you experience, recent major life events, medications, and dietary supplements you have been taking, and questions you would like to ask your doctor.
Samples of questions you want to ask your doctor.
- Do I have lymphoma? If so, which type and what stage is it?
- Is my condition severe?
- What tests and treatments should I have?
- What are the side effects of the tests and treatments?
- How long are the tests and treatments?
- After the treatments, can I continue going to work or resume my daily activities?